文本比较算法(二)
0
上一次我写了一个文本比较算法,发现效率非常低,而且内存消耗非常大,这里优化了一下。代码如下:
package com.acgist.nlp.query.compare;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.commons.collections.CollectionUtils;
public class Path {
private List<String> source;
private List<String> target;
private List<String> sourceTmp; // 临时
private List<String> targetTmp; // 临时
private boolean[][] map;
public Path() {
}
public Path(List<String> source, List<String> target) {
this.source = source;
this.target = target;
this.sourceTmp = new ArrayList<String>();
this.targetTmp = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long b = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Path path = new Path(Arrays.asList(new String[] {"B", "C", "X", "C", "A", "D", "F", "E", "S", "B", "A", "B", "C", "A", "C", "A"}), Arrays.asList(new String[]{"A", "B", "C", "A", "C", "A", "D", "F"}));
// Path path = new Path(Arrays.asList(new String[] {"A", "B", "C", "A", "C", "A", "D", "F"}), Arrays.asList(new String[]{"B", "C", "X", "C", "A", "D", "F", "E", "S", "B", "A", "B", "C", "A", "C", "A"}));
Path path = new Path(Arrays.asList(new String[]{"A", "B", "C", "A", "C", "A", "D", "F", "A", "B", "C", "A", "C", "A", "D", "F"}), Arrays.asList(new String[] {"B", "C", "X", "C", "A", "D", "F", "E", "S", "B", "A", "B", "C", "A", "C", "A"}));
path.execute();
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("消耗时间:" + (e - b) + "ms");
}
/**
* 执行比较
*/
public void execute() {
uniq();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(sourceTmp) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(targetTmp))
return;
map = new boolean[this.sourceTmp.size()][this.targetTmp.size()];
for (int x = 0; x < this.sourceTmp.size(); x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < this.targetTmp.size(); y++) {
if (this.sourceTmp.get(x) == this.targetTmp.get(y) || this.sourceTmp.get(x).equals(this.targetTmp.get(y)))
map[x][y] = true;
else
map[x][y] = false;
}
}
//==================打印二维数组=====================//
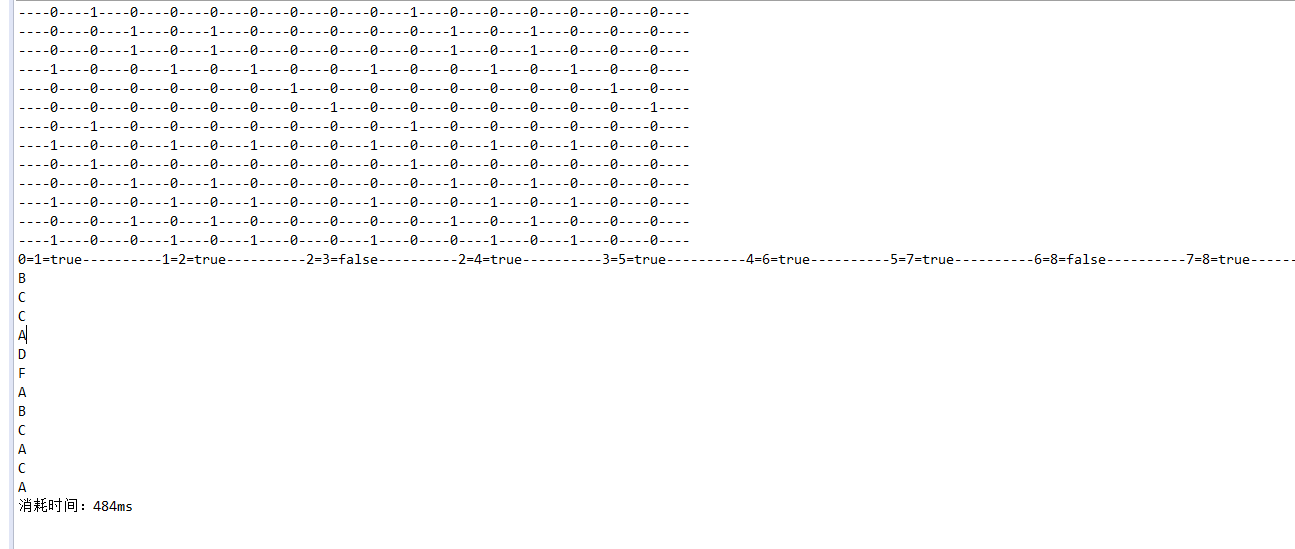
for (boolean[] bs : map) {
System.out.print("----");
for (boolean b : bs) {
System.out.print((b ? "1" : "0") + "----");
}
System.out.println();
}
//==================打印二维数组=====================//
List<Points> maxLengthPoints = new ArrayList<Points>();
for (int x = 0; x < this.sourceTmp.size(); x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < this.targetTmp.size(); y++) {
if(map[x][y])
maxLengthPoints.add(find(x, y, new Points(), null));
}
}
List<Points> maxPoints = maxPoints(maxLengthPoints);
maxLengthPoints.clear();
//==================打印最大路径=====================//
for (Points points : maxPoints) {
for (Point point : points.getPoints()) {
System.out.print(point.getX() + "=" + point.getY() + "=" + point.getSame() + "----------");
}
System.out.println();
}
//==================打印最大路径=====================//
Points points = optimal(maxPoints);
//==================打印最优路径=====================//
for(Point point : points.getPoints()) {
if(point.getSame())
System.out.println(this.sourceTmp.get(point.getX()));
}
//==================打印最优路径=====================//
}
/**
* 去掉两端没有匹配的元素
*/
private void uniq() {
for(int i = 0; i < this.source.size(); i++) {
String sourceV = this.source.get(i);
if(this.target.contains(sourceV))
this.targetTmp.add(sourceV);
}
for(int i = 0; i < this.target.size(); i++) {
String targetV = this.target.get(i);
if(this.source.contains(targetV))
this.sourceTmp.add(targetV);
}
}
/**
* 计算匹配数最大路径
*/
private List<Points> maxPoints(List<Points> maxLengthPoints) {
// 大的排前面
Collections.sort(maxLengthPoints, (Points a, Points b) -> {
if(a == null || b == null)
return 0;
if(a.getNumber() > b.getNumber())
return -1;
else if(a.getNumber() < b.getNumber())
return 1;
return 0;
});
int maxNumber = maxLengthPoints.get(0).getNumber();
List<Points> maxPoints = new ArrayList<Points>();
maxLengthPoints.forEach(points -> {
if(points.getNumber() == maxNumber)
maxPoints.add(points);
else
return;
});
return maxPoints;
}
/**
* 计算某点上最大路径
*/
public Points find(int x, int y, Points points, Points optimal) {
if(x == this.sourceTmp.size() || y == this.targetTmp.size()) {
if(optimal == null)
return points;
return optimal(points, optimal);
} else {
points.addPoint(new Point(x, y, map[x][y]));
if(map[x][y]) {
optimal = find(x + 1, y + 1, new Points(points.getNumber(), points.clonePoints()), optimal);
} else {
optimal = find(x, y + 1, new Points(points.getNumber(), points.clonePoints()), optimal);
optimal = find(x + 1, y, new Points(points.getNumber(), points.clonePoints()), optimal);
optimal = find(x + 1, y + 1, new Points(points.getNumber(), points.clonePoints()), optimal);
}
return optimal;
}
}
/**
* 计算最优路径
*/
public Points optimal(List<Points> maxPoints){
int index = 0;
float similarity = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < maxPoints.size(); i++) {
Points points = maxPoints.get(i);
float tmp = Float.valueOf(points.getNumber()) / Float.valueOf(points.getPoints().length);
if(tmp > similarity) {
similarity = tmp;
index = i;
}
}
return maxPoints.get(index);
}
/**
* 两点间选取最优
*/
public Points optimal(Points points, Points optimal) {
if(points.getNumber() < optimal.getNumber())
return optimal;
else if(points.getNumber() > optimal.getNumber())
return points;
else if((Float.valueOf(points.getNumber()) / Float.valueOf(points.getPoints().length)) < (Float.valueOf(optimal.getNumber()) / Float.valueOf(optimal.getPoints().length)))
return optimal;
else
return points;
}
}
class Points {
private int number;
private Point[] points;
public Points() {
}
public Points(int number, Point[] points) {
this.number = number;
this.points = points;
}
public void addPoint(Point point) {
if(points == null)
points = new Point[0];
points = Arrays.copyOf(points, points.length + 1);
if(point.getSame())
number++;
points[points.length - 1] = point;
}
public void clear() {
this.number = 0;
this.points = new Point[0];
}
public boolean isNotEmpty() {
return this.points != null && this.points.length != 0;
}
public Point[] clonePoints() {
return Arrays.copyOf(points, points.length);
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public Point[] getPoints() {
return points;
}
public void setPoints(Point[] points) {
this.points = points;
}
}
class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
private boolean same;
public Point() {
}
public Point(int x, int y, boolean same) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.same = same;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public boolean getSame() {
return same;
}
public void setSame(boolean same) {
this.same = same;
}
}
主要加了一个去掉完全不能匹配的字符,然后再开始匹配,效率就提升了很多,而且匹配更精确。
上一篇文章:http://www.acgist.com/article/262.html